|
 |


|
|
|
| Aspirin |
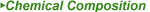 |
| White crystalline powder |
 |
| 50-78-2 |
 |
| Aspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid is asalicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication.Aspirin also has an antiplatelet effect by inhibiting the production of thromboxane, which under normal circumstances binds platelet molecules together to create a patch over damaged walls of blood vessels. |
 |
Product Name: Aspirin
Synonyms: o-Acetylsalicylic acid 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid
2-Acetoxybenzoic acid
aspirin usp
Aspirin
Acetoxybenzoic acid
Metronidazolum
2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid
2-(acetyloxy)benzoate
Acetyl Salicylic Acid
CAS: 50-78-2
EINECS: 200-064-1
MF: C9H8O4
MW: 180.15
Assay: 99.6%
Appearance: White crystalline powder, odourless, microstrip acid.
Melting point 136-140°C
Boiling point 321.4°C at 760 mmHg
Flash point 131.1°C
Water solubility 3.3 g/L (20°C)
Vapour Pressur 0.000124mmHg at 25°C
2. Descriptions:
Aspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid is asalicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication.Aspirin also has an antiplatelet effect by inhibiting the production of thromboxane, which under normal circumstances binds platelet molecules together to create a patch over damaged walls of blood vessels. Because the platelet patch can become too large and also block blood flow, locally and downstream, aspirin is also used long-term, at low doses, to help prevent heart attacks, strokes, and blood clot formation in people at high risk of developing blood clots.Also, low doses of aspirin may be given immediately after a heart attack to reduce the risk of another heart attack or of the death of cardiac tissue.Aspirin may be effective at preventing certain types of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer. |
|
|
|
|
|